What is a USB Operating System?
Overview
A USB Operating system means a live USB. A live USB is a mobile device that is plugged into a computer's universal serial bus (USB) port and runs an operating system on it without affecting the host system. These include consumer electronic devices like smartphones and storage systems like USB sticks and external hard disks.
LiveDistro or Live USB operating system is a distribution of any OS that can load and run on portable media. LiveDistro capabilities make it easier for users to transport their preferred operating system and utilize it on different machines. LiveDistros are typically based on Linux and are frequently used to run Linux-based OS on Windows-based machines without making any modifications to the host machine. Windows To Go is the first OS made by Microsoft that boots and runs on a USB device.
OS on a stick is another term used for the Live USB operating system. Due to the growing storage capabilities of portable devices like external hard disks, pen drives, etc. Users can now store not just the operating system but also the applications and the files, making the device effectively a computer on a stick.
How to Use an Operating System on a USB Stick?
Using Rufus on Windows or the Disk Utility on a Mac, you can install an OS onto a USB stick and use it like a computer. You'll need to format the USB drive, get the OS image (.iso file), and install the OS on the USB drive. Don't forget to switch the startup disc for Mac and enable USB booting in Windows BIOS!
Let's see the steps to install an OS onto a USB stick:
Making a Bootable Drive Using Rufus.
- In the BIOS, turn on USB booting. You can control the hardware in your computer with the use of the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). To enter the BIOS at startup, tap the relevant key (mostly F2 or Del). To get to the Boot tab, use the arrow keys. Fix USB drive option on the top using the Enter key. Your computer will reboot with the modified settings once you choose Save and Exit.
Note: Computers from various manufacturers use various forms of BIOS. For information on the relevant keys needed to access and modify the BIOS configuration, check your laptop manufacturer's manuals.
-
You need a USB drive with a minimum of 16 GB of space. If you want to fit anything on the drive beside the operating system, 32GB or more is advised. Also, USB 2.0 will function, but USB 3.0's faster speed is preferred.
-
The disc image (.iso file) of the operating system you want to install on the USB stick should be downloaded. You can find a list of download links for OS disc images at the bottom of the Rufus website under the heading Non-exhaustive list of ISOs Rufus is known to work with.
-
Download and launch Rufus. Because Rufus is an executable file, it simply has to be downloaded and launched.
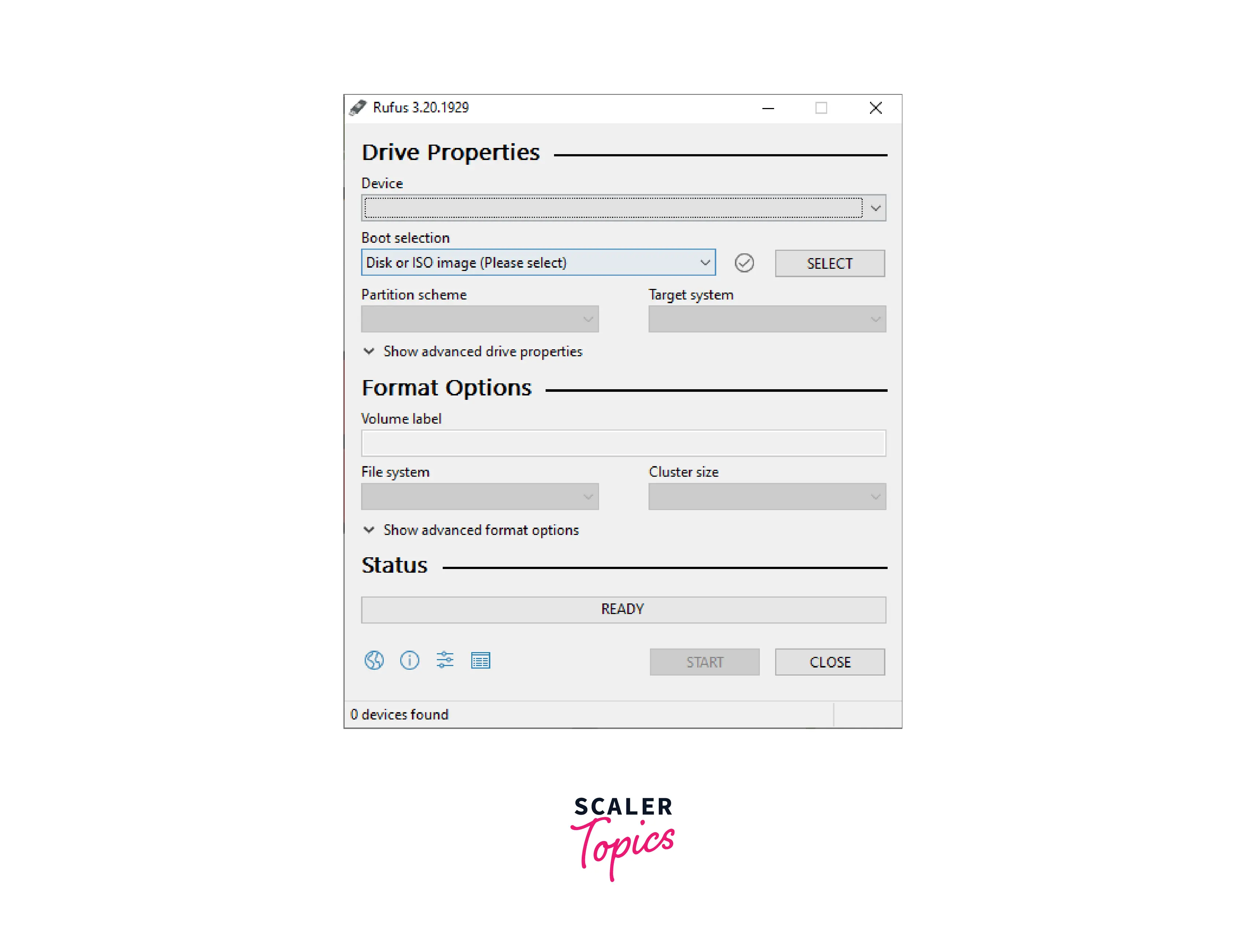
-
Plug your USB stick into the computer's USB port. It will show up in This PC with your other drives.
-
Choose your USB flash drive listed when you click the Device menu in the Rufus application.
-
Choose your Disk ISO image from the next SELECT option.
-
Choose MBR (Master Boot Record) from the Partition Scheme option and BIOS or UEFI will appear in the Target System. Older, but more prevalent, MBR disk structures are used extensively in Windows-based PCs. You can choose GPT (GUID Partition Table), a more recent technology, although some operating systems installations may not work with it.
-
In the File system option, if you're installing Linux to your bootable USB drive, use exFAT and if you're installing Windows, use NTFS.
-
Finally, click on the Start button, the progress bar will be shown below. When the procedure is finished, you'll be notified.
-
Restart your computer and test your bootable USB operating system. Your machine should use the USB drive to boot from the disc image if USB booting is enabled.
Note: The flash drive will be formatted during this procedure. If you want to save any of the data on your USB flash drive, copy it to your computer first. Also, selecting your startup disk can be done separately in some BIOS via a special menu. If you are experiencing difficulties booting into your flash drive, check with your manufacturer's requirements to get the specific details for using the BIOS menu.
What are the Most Useful Linux Distributions to Run from a Live USB Drive?
Linux operating system portable versions perform incredibly well on USB devices. Following are the Linux distributions that are the most used for live USB drives:
- Puppy Linux: A lightweight Linux-based OS for live USB.
This USB Operating system belongs to the collection of lightweight Linux distributions with a focus on improving usability and small memory usage.
Puppy Linux has only been regarded as a curiosity for a while. It could smoothly run on early Pentium PCs without tiring out because it was made to be utilized on the most basic hardware machine. But that wasn't very useful, many did so merely to test their ability to install Puppy Linux on their outdated hardware.
However, new versions of Puppy Linux and updates are still released frequently. It is still minimal and is designed for underpowered hardware systems. Also, you can now do tasks by installing Puppy Linux on a USB stick.
- elementary OS: A more modern Desktop Experience
elementary USB Operating system provides a hybrid OS made of Mac's operating system with the well-known GNOME desktop environment. You can take up the experience on your own with just a few clicks because it is that simple.
AppCenter offers software designed exclusively for elementary OS like LibreOffice, the image editor, etc. You can be sure you won't run into any device compatibility issues because Ubuntu and elementary OS are very similar. Additionally, it performs flawlessly even on outdated technology, such as Atom and Celeron-powered computers.
- GParted Live: A lightweight tool for managing the partitions.
GParted is a popular Linux program for managing the hard disk partitions. A lot of Linux distributions already have this installed, otherwise, a copy of GParted is required that can be loaded from a USB stick.
It's a Linux distribution for your USB drive named GParted Live. By using this small tool, you can resize your hard disk as needed. But be careful—one slip-up might potentially prevent your hard drive from booting.
- Sugar on a Stick: An educational purpose OS for children
A free software project called Sugar was created keeping children in mind. The objective is to deliver an experience that promotes communication, observation, and learning. Sugar USB operating system was originally a component of the One Laptop Per Child effort. However, Sugar OS is now a project under the Software Freedom Conservancy.
While Sugar can be installed straight to a hard drive, a copy can also be used as a live USB OS. The group actively promotes USB operating system and has developed Sugar on a Stick, a variation of the OS.
- Ubuntu GamePack: A portable gaming setup OS
LiveDistro is not just about completing tasks with USB sticks. Sometimes, you may simply want to have fun. Your USB drive can act as a portable gaming PC with Ubuntu GamePack OS. While the specifications of the machine you're borrowing may limit you, as long as you stick to games with low system needs, you shouldn't encounter many issues.
Conclusion
- A live USB is a portable device that is connected to a computer's universal serial bus (USB) port and runs an operating system (OS).
- Users can store not just the operating system but also the applications and the files on a USB stick, making the device effectively a computer on a stick.
- Portable USB stick computers are build by installing an OS on the USB stick. Use Rufus software on Windows or the Disk Utility on a Mac for the installation process, and this process will require an OS image (.iso file) to install the specific OS.
- Linux USB operating system versions perform incredibly well on portable devices. These are some of the most used OS for live USB drives, Puppy Linux, elementary OS, GParted Live, Sugar on a stick, and Ubuntu GamePack.
