What Does a Cyber Security Analyst Do?
A cyber security analyst is a professional who is responsible for identifying, preventing, and mitigating cyber security threats to an organization.
A Cyber Security Analyst plays a crucial role in protecting the organization’s critical and sensitive information, network infrastructure, and the entire system from illicit access, abuse, breach, and disruption.
The job of a cyber security analyst requires an optimal blend of technical and analytical skills. They must deeply understand the various types of cyber threats and their respective mitigation techniques.
They must also have the ability to analyze given data and identify patterns that may potentially lead to a threat.
The first and foremost responsibility of a cyber security analyst is to protect the organization’s networks and systems from cyber-attacks.
This includes monitoring for potential threats, such as malware, ransomware, viruses, and hacking attempts, and taking proper preventive measures to mitigate them.
They may also be responsible for implementing security measures, such as firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems(IDS), Intrusion Prevention Systems(IPS), endpoint detection and Data Loss Prevention(DLP) solutions to protect the organization’s infrastructure.
How to Become a Cyber Security Analyst?
The path to becoming a cyber security analyst typically involves a combination of education, experience, and certifications. Here are the few steps that will be helpful to become a cyber security analyst:
- Education: This is the first step towards becoming a cyber security analyst. One should obtain a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as information technology, computer science or cyber security. A candidate may be preferred with other degrees too if they have relevant experience or certifications.
- Experience: A cyber security analyst learns a lot by experience than education or certifications. Experience can be gained through internships, freelance engagements, or entry-level positions in IT or security. It is one of the most essential and crucial steps for building the skills and knowledge needed to become a cyber security analyst.
- Certifications: Certificates demonstrate an individual’s knowledge and skills in the field and can make them stand out in front of potential employers. Many employers prefer candidates who have certifications in cyber security. Some of the most popular certifications for cyber security analysts include CISSP, CISA, CEH, OSCP, GCIH, CISM and CompTIA Security+. Certificates like eJPT, eWPT, and PNPT are also gaining popularity these days.
- Competitions: Participating in competitions is a great way to improve skills. Individuals willing to become cyber security analysts should participate in CTF (capture the flag) competitions, bug bounty hunting and exploit development competitions. These competitions help an individual to gain practical experience that no degree or certificate will teach.
- Networking: Networking is important to becoming a cyber security analyst. Individuals learn a lot through interaction with senior professionals.
Volunteering in organizations such as the Information Systems Security Association (ISSA), DefCon, the International Association of Computer Science and Information Technology (IACSIT) or The International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)2 will provide opportunities to connect with other professionals in the field and stay current on the latest developments.
What are the Roles and Responsibilities of a Cyber Security Analyst?
The day-to-day responsibilities of a cyber security analyst can vary depending on the organization and the specific role they are in. However, some common tasks include:
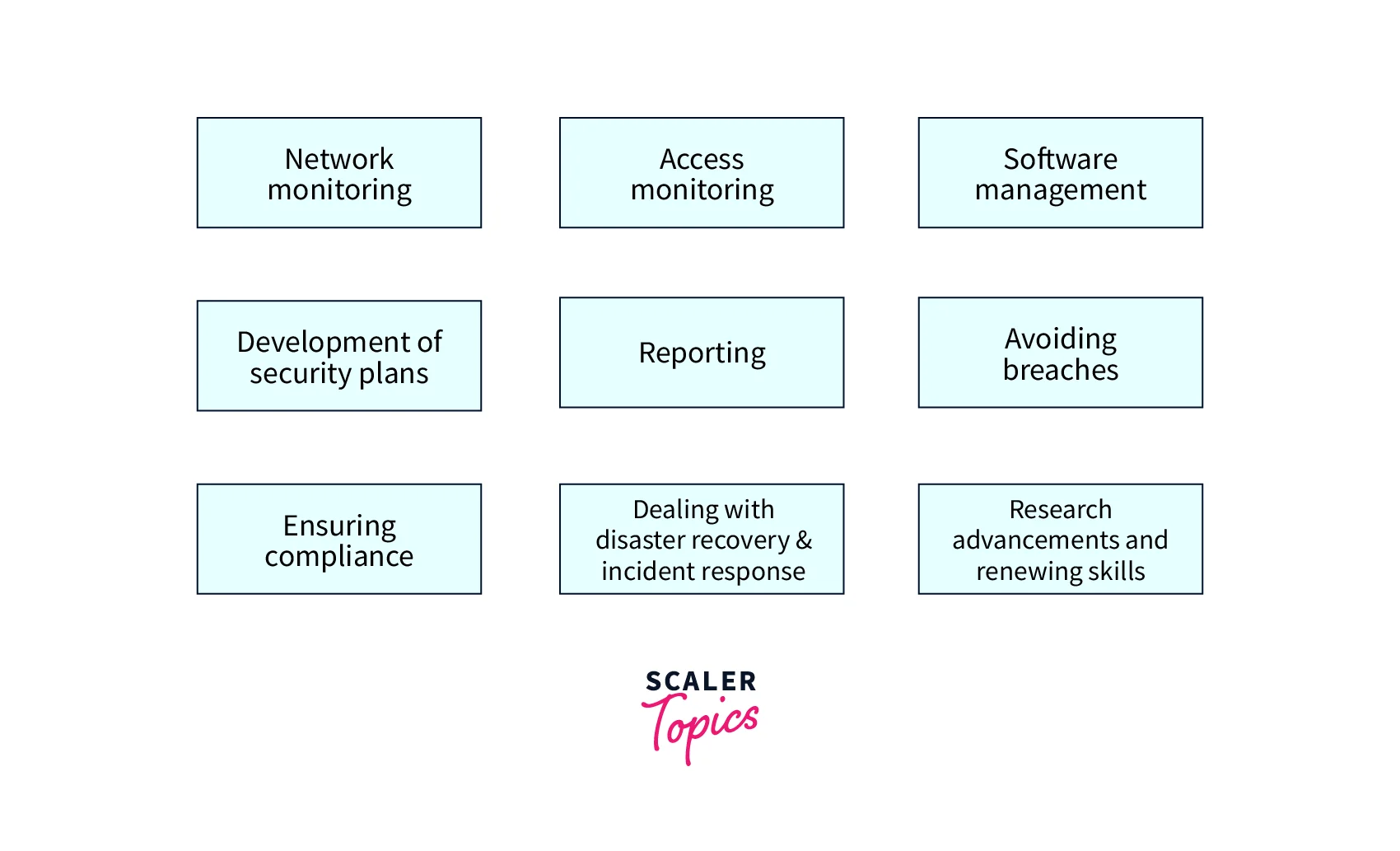
- Monitoring: Cyber security analysts have to monitor networks and systems for potential threats, such as malware, ransomware, viruses, and illicit hacking attempts. Various tools and techniques are used by cyber security analysts to analyze potential threats and take proper action to prevent or mitigate them.
- Security measures: Cyber security analyst is responsible for implementing security measures to protect the organization’s infrastructure. This may include solutions such as firewalls, VPNs, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR).
- Security awareness training and guidance: Cyber security analysts are responsible for providing awareness training and guidance to other members of the organization on how to identify and prevent cyber threats. They may also be responsible for guiding how to respond to a cyber incident. Phishing awareness training is a common exercise that is carried out in all organizations.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT): A VAPT activity is composed of two steps, the first is the assessment of vulnerabilities and the second is penetration testing. An individual conducting a VAPT exercise assesses the target system for vulnerabilities and then tries to gain access to the system through hacking attempts. Cybersecurity analysts are responsible for conducting regular assessments of the organization’s security posture. This includes identifying vulnerabilities in the organization’s networks and systems and recommending solutions to mitigate them.
- Incident response: Cyber security analysts are responsible for responding to cyber incidents, such as data breaches or hacking attempts. They must be able to quickly identify the cause of the incident and take action to contain and mitigate the damage. This is a 24*7 responsibility and can be exhaustive sometimes.
- Reporting and documentation: Cybersecurity analysts are also responsible for reporting and documenting their findings, recommendations, and actions are taken. They must be able to provide clear and concise reports on their findings and make recommendations based on their analysis.
- Keeping up to date: Cyber security analysts are also responsible for keeping up to date with the latest developments and trends in the field of cyber security. This includes staying current on the latest threats and vulnerabilities and adapting to new technologies and best practices.
- Collaboration: Cybersecurity analysts often work in teams, and they must be able to collaborate effectively with other members of the organization. They may work with other IT professionals, such as network administrators and system administrators, as well as with management and other stakeholders.
Important Skills of a Cyber Security Analyst
A cyber security analyst must have a blend of technical and analytical skills, as well as strong communication skills. Some important skills of a cyber security analyst are:
- Technical skills: A cyber security analyst must have a deep understanding of computer networks and systems. They must be well versed with various operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and macOS, and should be familiar with networking protocols, such as TCP/IP and DNS. They should also have experience working with security tools, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Sometimes cyber security analysts are also required to develop their tools or automate redundant tasks. Knowledge of a good scripting language such as python is very important for a cyber security analyst.
- Analytical skills: Cybersecurity analysts must have strong analytical skills to be able to analyze data and identify patterns that may indicate a potential threat. They must also be able to make recommendations based on their analysis.
- Communication skills: Cybersecurity analysts must be able to explain technical concepts to non-technical individuals and must be able to work effectively with other members of the organization. They must also be able to provide clear and concise reports on their findings.
- Cybersecurity knowledge: Cybersecurity analysts must have a deep knowledge of cybersecurity concepts, best practices, and trends. They should be familiar with various types of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and social engineering, and should understand how to mitigate them.
- Risk management: Cybersecurity analysts must have a good understanding of risk management concepts and be able to identify, evaluate, and prioritize risks to the organization.
Salary of a Cyber Security Analyst
The average salary for a cyber security analyst can vary depending on several factors, including the level of experience, location, and industry. According to data from Payscale, the average salary for a cybersecurity analyst in the United States is $72,000 per year. However, this can vary greatly depending on the level of experience.
- Entry-level cyber security analysts: According to Glassdoor, the average salary for an entry-level cyber security analyst is $66,000 per year. However, this can vary depending on the location and industry.
- Mid-level cyber security analysts: According to Payscale, the average salary for a mid-level cyber security analyst is $86,000 per year. However, this can vary depending on the location and industry.
- Senior-level cyber security analysts: According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a senior-level cyber security analyst is $110,000 per year. However, this can vary depending on the location and industry.
It is important to note that these figures are only averages and may not reflect the specific salary for a particular position. Factors such as location, industry, and level of experience can greatly impact the salary of a cybersecurity analyst. Additionally, it is important to note that factors such as certifications, skills, and additional responsibilities may also affect the salary of a cybersecurity analyst.
Qualifications and Certifications Required to Become a Cyber Security Analyst
To become a cyber security analyst, one typically needs to have a bachelor’s degree in a related field such as computer science, information technology, or cyber security. Some employers may also consider candidates with degrees in other fields, such as mathematics or engineering if they have relevant experience or certifications.
In addition to a bachelor’s degree, many employers also prefer candidates who have certifications in cyber security. Some of the most popular certifications for cyber security analysts include:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): This is a widely recognized certification that demonstrates an individual’s knowledge and experience in information security.
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): This certification is for professionals who audit, control, monitor and assess an organization’s information technology and business systems.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): This certification is for professionals who can identify and exploit vulnerabilities in networks and systems.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): This certification is for professionals who manage, design, and oversee an organization’s information security.
- GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH): This certification is for professionals who can identify, respond to, and handle security incidents.
- CompTIA Security+: This certification is for professionals who have a foundational knowledge of security concepts and best practices.
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP): This certification is offered by the Offensive Security group. It is recommended for professionals who are willing to make a career in offensive security.
- eLearnSecurity Junior Penetration Tester (eJPT): The INE group offers this certificate. It is recommended for individuals interested in penetration testing.
It is important to note that certifications are not always required to become a cybersecurity analyst, but they can be beneficial in demonstrating one’s knowledge and experience in the field to potential employers. Additionally, many employers may require their analysts to maintain their certifications through continuing education and re-certification exams. Learn more about cyber security in our blogs.
Conclusion
The field of cyber security is constantly evolving, and cyber security analysts must keep up with the latest developments. They must stay up-to-date on the latest cyber threats and security trends and must be willing to continuously improve their skills. In conclusion, the role of a cyber security analyst is essential for any organization looking to protect itself from cyber threats. They are responsible for identifying, preventing, and mitigating cyber threats to an organization’s networks and systems, as well as its sensitive information. They must have a combination of technical and analytical skills, as well as strong communication skills. With the constant evolution of cyber threats, cyber security analysts must be willing to continuously improve their skills to stay ahead of the game.
