What is the Correct HTML for Creating a Hyperlink?

What is the Correct HTML for Creating a Hyperlink ?
In HTML, the correct way of creating a hyperlink is to use the anchor tag which is represented by the <a> symbol. The hyperlink is used for redirecting to a new URL which can be a web page, file, or the same location within the web page. The content that we write in the <a> tag defines the location of the hyperlink. The URL should be written inside the href attribute of the anchor tag.
How to Insert Hyperlink in HTML Page ?
To insert a hyperlink we use the anchor tag represented by <a> and the text is inserted in the <a> and </a> tags. The href attribute is used to write the URL. The anchor tag should be used within the body tag.
Syntax :
Example
If we want to create a hyperlink to Google's website, we will insert its URL in the href attribute. The content that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage.
Output :

We can see that a hyperlink is created that redirects to the URL mentioned in the href attribute when clicked.
Default Appearance of the HTML Anchor Tag
- The visited link is marked as purple.
- The unvisited link is marked as blue which is the default color of a hyperlink.
- An active link is marked as red.
Attributes
Global Attributes
Global attributes include those attributes which can be used with all the elements in HTML.
The anchor tag supports the global attributes in HTML.
Event Attributes
The event attributes are used to define event actions in HTML. The anchor tag supports all the Event Attributes in HTML.
The other attributes are :
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| href | This attribute is used to specify the URL or the hyperlink. |
| hreflang | This attribute is used to specify the language of the linked URL. |
| type | This attribute is used to specify the media type of the linked URL. |
| target | This attribute is used to specify the location where the linked hyperlink should be opened. |
| download | This attribute is used to download the mentioned URL. The user needs to click the hyperlink to download it. |
| ping | This attribute is used for a list of URLs separated by a space. When the link is clicked, the browser will send POST requests with the body PING to the given hyperlinks. This command is used for tracking. |
| rel | This command is used to specify the relation between the current document and the linked document. |
| referrerpolicy | This attribute is used to specify which referrer information should be sent with the URL. |
| media | This attribute is used to specify the media or device for which the URL is optimized. |
Properties
Content Categories :
- Flow Content :
It is a broad category that contains all those elements that can be used inside the body tag. It includes elements like heading elements, interactive elements, embedding elements, phrasing elements, sectioning elements, and form-related elements.
For example, an anchor tag is included in the category of flow content elements. - Phrasing Content :
Phrasing content is a subset of flow content that is used to define the text and the markup it contains, and it can be used where the flow content is expected. The anchor tag belongs to this category if it contains only the phrasing content. - Interactive Content :
Interactive content is another subset of flow content that includes those elements that are particularly designed for user interaction, and are used where the flow content is expected. The anchor tag belongs to this category as well.
Tag Omission :
Not allowed. Both opening and closing tags are compulsory.
Allowed Parents :
Other <a> elements are not allowed but elements accepting phrasing content or flow content are allowed.
DOM Interface :
HTMLAnchorElement
More Examples
Example : 1 - Linking to an Absolute URL
An absolute URL contains the entire address of the site and has HTTP/HTTPS protocol added to the domain name.
Output :

Example : 2 - Linking to Relative URLs
The relative URL does not contain the full web address and only contains the location following the domain. It assumes that the URL that we have added is on the same site and is part of the same root domain.
It starts with the forward-slash and makes the browser stay within the current site.
Output :

Example : 3 - Linking to an Element on the Same Page
To link the URL to an element on the same page, we set the href attribute to an id of an element to where we want to navigate.
Before clicking on the link :

After clicking on the link :
When we click on the link, the page focus goes down and points where the id of that element matches the set id. In our example, when we click the link href is set as #divs, and the focus goes to the paragraph where the id matches #divs.

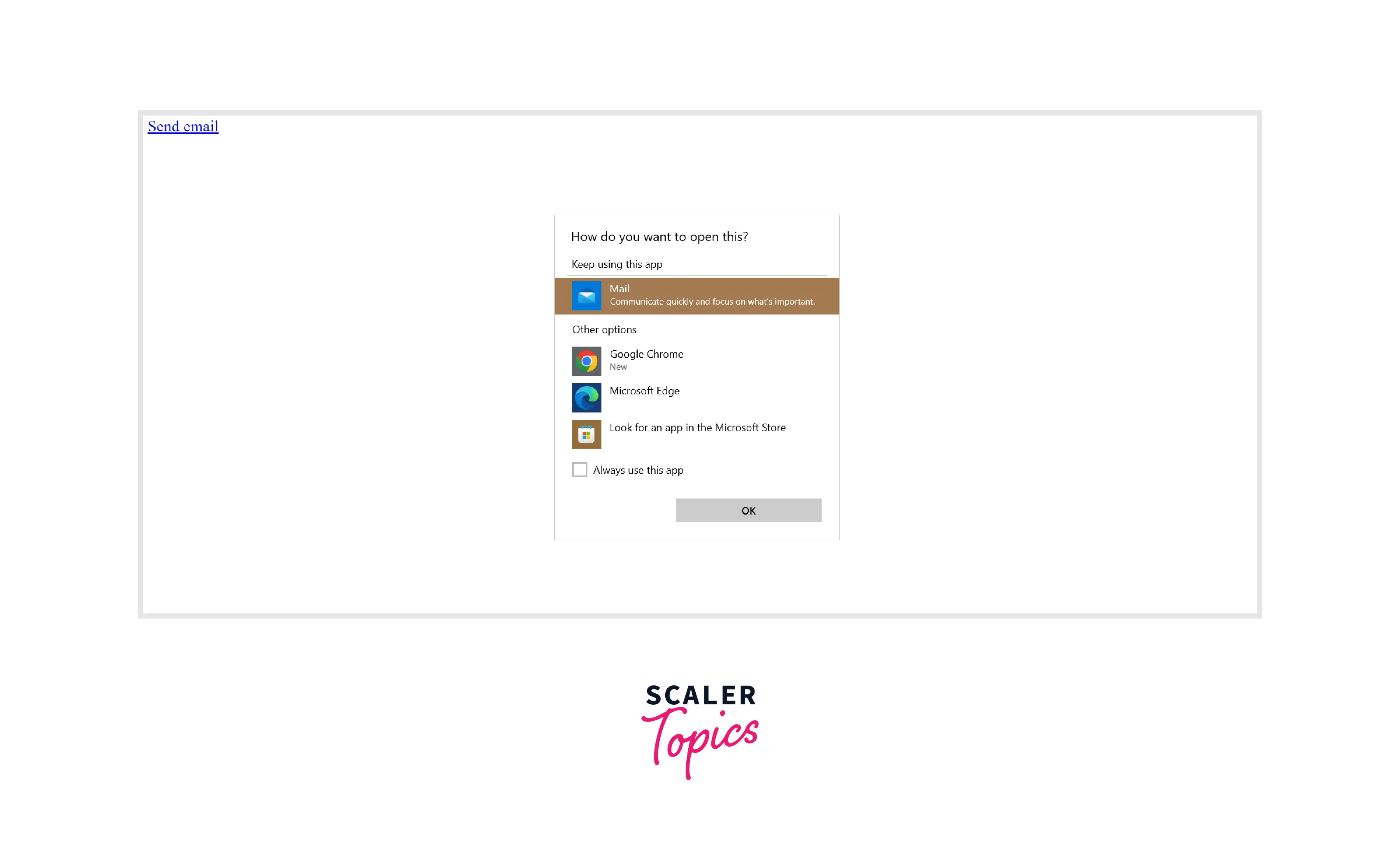
Example : 4 - Linking to an Email Address
To create links that open externally in the user's email program , we use the mailto: scheme.
Output :
On clicking the link, a pop-up comes.
Example : 5 - Linking to Telephone Numbers
If we want to link a phone number, we will insert it in the href attribute. The content that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage.
Output :

We can see that a hyperlink is created that redirects to the number mentioned in the href attribute when clicked.
Note :
The tel : link behavior varies with device capabilities :
- If the device is a cellular device, it auto-dials the number.
- Many operating systems make calls using Skype or FaceTime.
- Other behaviors can include number saving and sharing.
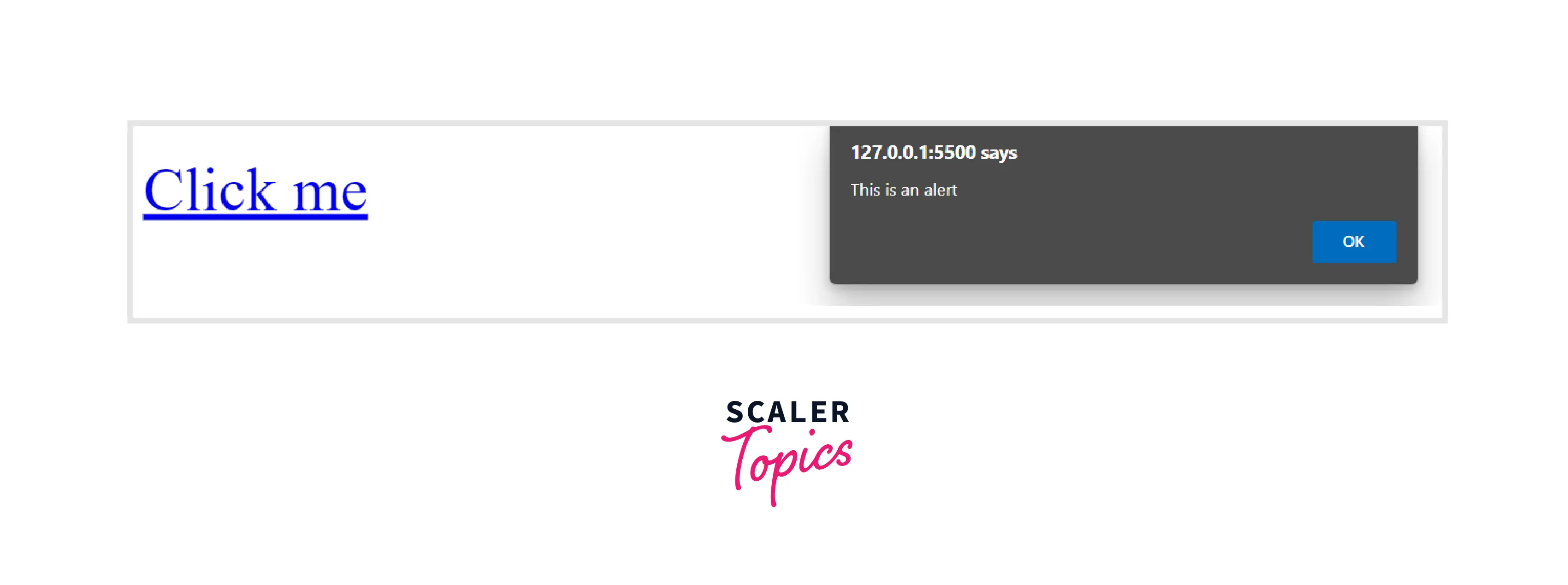
Example : 6 - Linking to a JavaScript
If we want to link our URL to a JavaScript page, we will insert the text in the href attribute. The content that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage.
Output :
On clicking on the link, an alert comes up.
Example : 7 - Linking to a Non-HTML Resource
If we want to link to a non-HTML resource like an external file like a word document or PowerPoint, we will insert its path in the href attribute. The content that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage.
Output :

When we click on the link, it will redirect to the word document whose path we have provided.
Example : 8 - Using the Download Attribute to Save a "canvas" as a PNG
If we want to download a canvas that we have painted, we will handle it using the 'download' attribute which tells us by what name the painting will be saved on the device. A canvas is created.
HTML:
CSS:
In the following code, we are setting the background color of the canvas and the color of the a tag.
JavaScript:
First, we decide the color of the ink, then add some action listeners for specific actions and write a function to fill the arc.
Output :

Example : 9 - Using an Image as a Link
If we want to link to an image, we will insert its details using an img tag nested inside the anchor tag. The details of the image that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage. The src attribute of the img tag is used to write the path name of the image.
Output :

Example : 10 - Opening a Link in a New Browser Window
If we want the URL to open in a new browser window, we will insert its path in the href attribute and set the target attribute as _blank. The content that we want to show will be written between the anchor tag which will be displayed on the webpage.
Output :
On clicking the link, it gets opened in a new window.

Skip Links
Skip links take the user to the main content, past the various elements like the logo, search, and navigation. It is usually hidden until it receives focus.
Skip links are used to skip the repeated content like headers, paragraphs, etc. It is useful for those who navigate through the pages with the help of assistive technology like switch control, voice command, etc. as moving through the repetitive links can be tedious.
HTML:
CSS:
Default CSS Settings
The default CSS setting of the "a" tag for most of the browsers is :
Size and Proximity
Links should provide a large area so that it is easy to activate them. This not only helps those with motor control issues but also touchscreen users. A size of at least 44×44 pixels is expected.
Links should have proper spacing between them. When there are multiple links nearby, the wrong link might get clicked, so it is recommended to have proper spacing between the links.
Security and Privacy
In order to open the link in a new window, target = "blank" is used. But this can lead to a window.opener API exploration attack. It is recommended to use rel = "noreferrer" and rel = "noopener" so that the threat can be protected.
Accessibility
Accessibility is to make the websites usable by as many people as we can in different ways like :
- tablets, mobile phones.
- alternating browsing devices like TV, and smartwatches.
- phones using old browsers.
- by including features for various people having visual, hearing, mobility, and cognitive impairments so that they can access the page.
Anchor tags are also used as buttons by setting their href attribute as javascript:void(0) or "#" to prevent the page from refreshing and then listening to the click events. This causes unexpected behavior when links are copied/dragged, opened in a new tab or window, bookmarked, etc. So it is not recommended to use the href attribute as a button.
While writing the code, for the anchor tag, the content inside it should indicate where the link goes.
Specifications
As mentioned above, it supports flow content, phrasing content, and interactive content. It also supports the global and event attributes in HTML.
Browser Support
The anchor tag in HTML is supported by the following browsers :
- Google Chrome 12
- Microsoft Edge 79
- Safari 6
- Opera 15
- Mozilla Firefox 49
- Samsung Internet
Conclusion
- In HTML, the correct way of creating a hyperlink is to use the anchor tag which is represented by the <a> symbol.
- The hyperlink is used for redirecting to a new URL which can be a web page, file, or the same location within the web page.
- To insert a hyperlink we use the anchor tag represented by <a> and the text is inserted in the <a> and </a> tags.
- It supports flow content, phrasing content, and interactive content. It also supports the global and event attributes in HTML.
- Links should provide a large area so that it is easy to activate them. It should also have spacing between them.
